In NFTs, traits—also known as attributes or properties—are distinct characteristics that define an NFT’s uniqueness. They are pivotal in establishing the rarity, visual appeal, and occasionally the utility of the NFT. Traits are especially significant in collections such as trading cards, generative art, or gaming assets, where individuality enhances value.
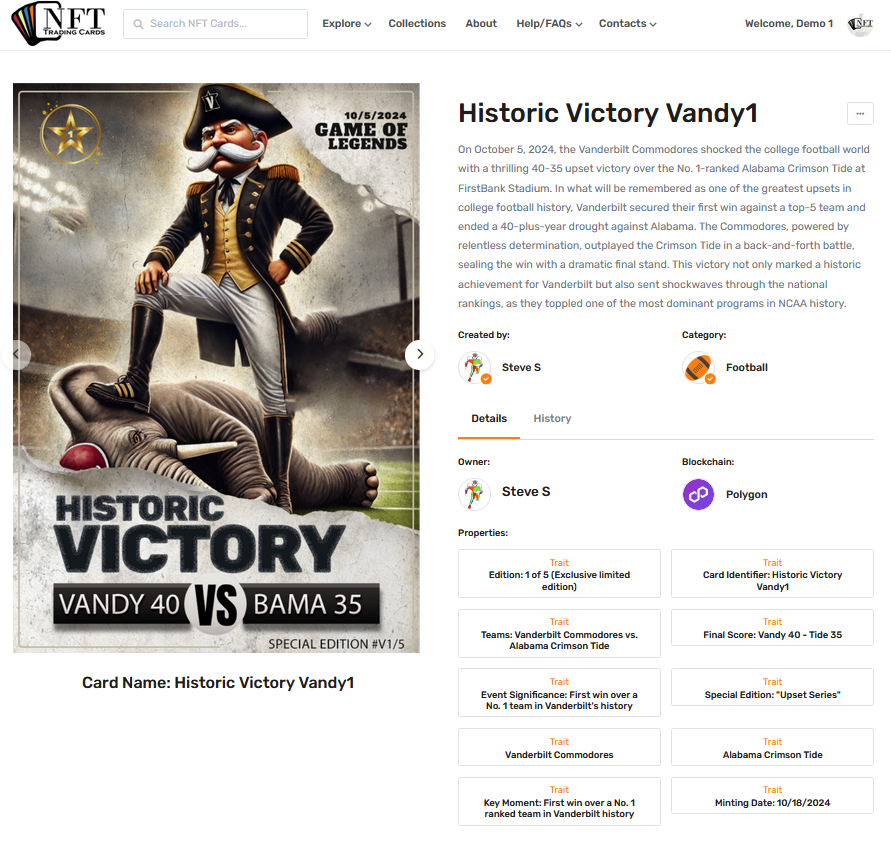
Key Aspects of NFT Traits
- Descriptive Features:
- Traits describe visual or functional elements of the NFT (e.g., color, background, accessories).
- These are often used in metadata to make each NFT distinct.
- Rarity Tiers:
- Some traits are common, while others are rare or even unique (1-of-1).
- Rarity can greatly impact the perceived and market value of the NFT.
- Categories of Traits:
- Visual Traits: Appearances, colors, patterns, and themes.
- Functional Traits: Abilities, utilities, or interactions tied to the NFT.
- Contextual Traits: Historical, thematic, or narrative-based features.
Examples of NFT Traits
Visual Traits
These define the appearance of the NFT.
- Backgrounds: Gradient, abstract, space, cityscape
- Colors: Vibrant, monochrome, metallic
- Accessories: Hats, glasses, jewelry
- Character Design: Hair color, pose, outfit
- Special Effects: Glow, shadows, animated particles
Functional Traits
These define what the NFT can do or unlock.
- Abilities: Speed, strength, magic powers (common in gaming NFTs)
- Access: VIP event tickets, exclusive content
- Interactivity: Changes based on user input or time of day
- Utility: Discount codes, staking benefits
Contextual Traits
These add narrative or thematic depth.
- Edition: Common, rare, legendary, 1-of-1
- Themes: Fantasy, futuristic, historical, minimalist
- Event-Based: Holiday specials, limited-time releases
- Cultural Ties: References to art, music, or heritage
Why Traits Are Important
- Determining Rarity:
- Traits define how common or unique an NFT is within a collection.
- Example: If only 1% of NFTs in a collection have a golden crown, it becomes a sought-after rarity.
- Adding Value:
- NFTs with rare or desirable traits often command higher prices.
- Example: An animated NFT or one with a holographic effect may sell for more.
- Enhancing Personalization:
- Traits allow collectors to choose NFTs that align with their preferences or identity.
- Utility and Engagement:
- Functional traits add utility, like access to communities, gaming perks, or real-world benefits.
Trait Rarity Framework
- Common Traits: Found in most NFTs (e.g., plain backgrounds).
- Uncommon Traits: Less frequent but not extremely rare (e.g., metallic finishes).
- Rare Traits: Unique or found in a small percentage (e.g., animated features, special themes).
- One-of-a-Kind (1/1): Exclusive, often hand-designed NFTs.

Leave a Reply